Cooling down ushers in a high incidence of heart attacks, and stem cells help with heart health
Every November to January is the peak of myocardial infarction, especially when the temperature drops sharply in autumn and winter, the incidence rate of myocardial infarction will rise suddenly. The weather is getting colder and the temperature is decreasing; Cold itself can lead to an increase in blood pressure, and in addition, very cold can cause vasoconstriction, induce myocardial ischemia, stimulate plaque rupture, and form blood clots, thereby causing myocardial infarction or cerebral infarction.
About myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction, also known as myocardial infarction, generally refers to acute myocardial infarction. It is myocardial necrosis caused by acute and persistent ischemia and hypoxia in the coronary artery.
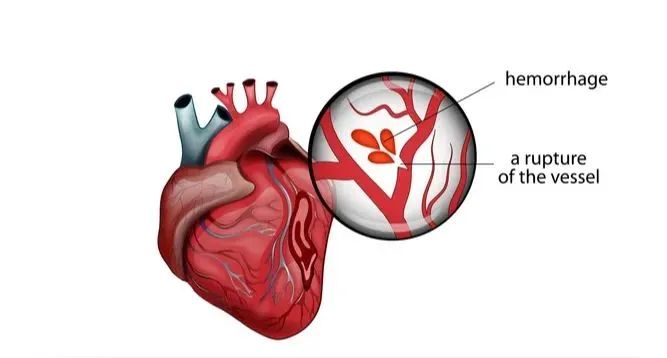
Myocardial infarction, as a serious winter season high incidence cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, has become a "cold-blooded killer" that takes away the lives of middle-aged and elderly people like a demon.
Be wary of several signs of myocardial infarction
Acute myocardial infarction occurs suddenly, but more than 50% of patients may have some premonitions before the onset of the infarction.
Atypical symptoms may also occur and are easily overlooked.

Such as paroxysmal chest pain, back pain, toothache, upper limb soreness, and upper abdominal pain, ranging from 3 to 10 minutes each time, accompanied by sweating or chest tightness, fatigue, and in severe cases, a feeling of impending death. When the attack occurs, it is deadly, and after relief, it becomes like a normal person without any discomfort. It can recur, once a few days, or multiple times a day.
Its harmfulness lies in the fact that there is no discomfort after relief, and many people continue to work and socialize, resulting in sudden exacerbation that cannot be relieved, leading to myocardial infarction, disability, and in severe cases, sudden death.
How to prevent myocardial infarction
Firstly, lifestyle needs to be improved, with special attention to diet. Smoking should be stopped, drinking a small amount of alcohol, consuming a low salt diet, and reducing sugar. At the same time, we should treat other basic diseases, such as hypertension and diabetes. Pay attention to prevention and regular physical examinations, especially for middle-aged and elderly people. It is recommended to have regular physical examinations every year.
Maintain a calm mindset, develop good lifestyle habits, and avoid prolonged overtime and staying up late. Dietary nutrition, reasonable diet, engage in moderate intensity physical activity at least 3-5 times a week, for at least 30-45 minutes each time.

Treatment methods for acute myocardial infarction
How to cure it? At present, the treatment of myocardial infarction includes drug therapy, interventional therapy, surgery, etc. These treatments can improve the symptoms of myocardial ischemia and heart failure, allowing occluded blood vessels to reopen. However, there is still no effective method to restore the function of the damaged heart. Although heart transplantation can replace damaged hearts, it is difficult to promote clinically due to the difficulty in selecting donors.
Stem cells protect the circulatory system
Stem cells are seed cells in the human body that can differentiate into all cells, including functional cells that make up the circulatory system.
Young and healthy stem cells injected into the body can differentiate into all the cells that make up the circulatory system, replace diseased and necrotic cells, gradually restore the normal physiological structure and function of the blood and heart, protect the circulatory system, and have excellent effects in preventing and treating diseases such as coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction.
With the development of regenerative medicine, stem cell transplantation has been proven to promote the regeneration of myocardial cells in the infarcted area, and treat myocardial infarction from the source. In particular, mesenchymal stem cells play an important role in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, characterized by:
1. Mesenchymal stem cells are a type of adult stem cells that have a wide range of sources, are easy to isolate and expand in vitro, have strong tissue repair ability, and can differentiate into multiple directions;
2. Mesenchymal stem cells can differentiate into tissue-specific cells, functionally related cells, and regulatory cells, while myocardial cells belong to tissue-specific cells;
3. Mesenchymal stem cells have the potential to repair tissues or cells, which can be manifested in promoting neovascularization, reducing infarct size and scar formation, and improving myocardial contractility. Paracrine function is one of the reasons why stem cells exert these functions;
4. Mesenchymal stem cells have low immunogenicity and can interact with various immune cells to regulate immune function.
At present, research has shown that mesenchymal stem cell transplantation, with its powerful repair and secretion functions, has a great promoting effect on the repair of myocardial cells and the recovery of cardiac function. At the same time, it also demonstrates the safety and effectiveness of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation as a substitute therapy.
 中文
中文
 English
English




